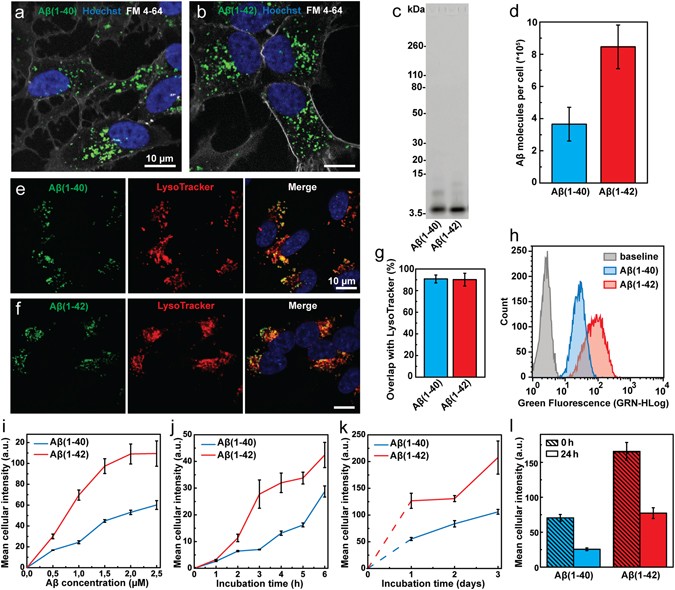
Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin-independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ(1–40)

Uptake of Aβ by OATPs might be a new pathophysiological mechanism of Alzheimer disease, BMC Neuroscience

Contribution of syndecans to cellular internalization and fibrillation of amyloid-β(1–42)
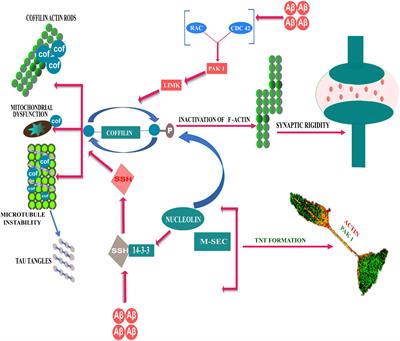
Frontiers Membrane interaction to intercellular spread of pathology in Alzheimer's disease

Misfolded amyloid-β-42 impairs the endosomal–lysosomal pathway

Uptake of Aβ by OATPs might be a new pathophysiological mechanism of Alzheimer disease, BMC Neuroscience
Interplay between Cellular Uptake, Intracellular Localization and the Cell Death Mechanism in Triphenylamine-Mediated Photoinduced Cell Death

Lipids uniquely alter the secondary structure and toxicity of amyloid beta 1 –42 aggregates - Zhaliazka - 2023 - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library

Designed Cell-Penetrating Peptide Inhibitors of Amyloid-beta Aggregation and Cytotoxicity - ScienceDirect

Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin- independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ (1–40)

Towards the integrative theory of Alzheimer's disease: linking molecular mechanisms of neurotoxicity, beta-amyloid biomarkers, and the diagnosis
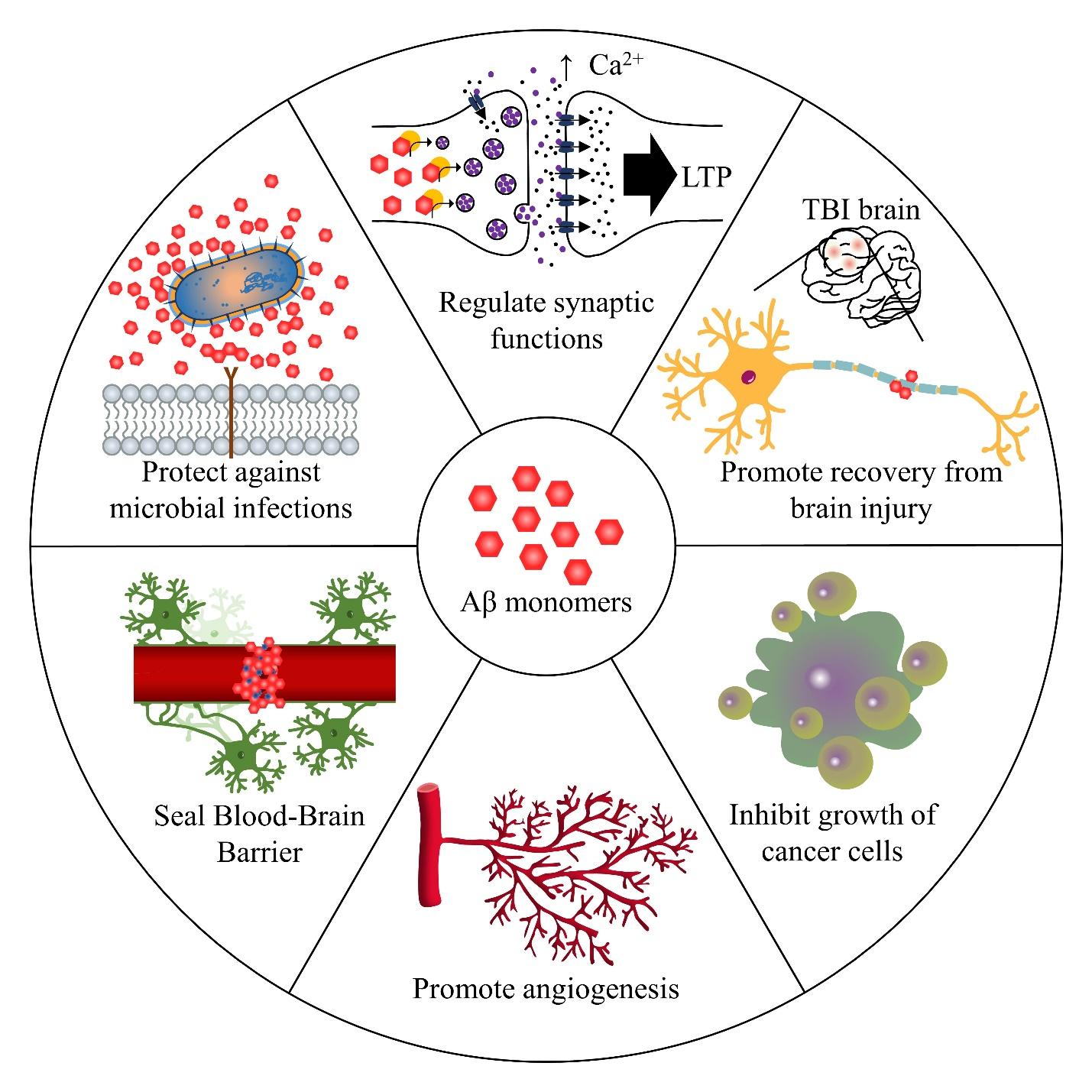
Physiological Roles of Monomeric Amyloid-β and Implications for Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutics

IJMS, Free Full-Text