probability - Proof explanation - weak law of large numbers

Let $(X_i)$ be i.i.d. random variables with mean $\mu$ and finite variance. Then $$\dfrac{X_1 + \dots + X_n}{n} \to \mu \text{ weakly }$$ I have the proof here: What I don't understand is, why it

Law of Large Numbers: What It Is, How It's Used, Examples

i.ytimg.com/vi/Yh5bR7X3ch8/sddefault.jpg

SOLVED: Let X1, X2 be independent and identically distributed random variables with E(Xi) = p, and let Sn = Σ(Xi - p). Assume that the moment generating function Mx(t) of X exists

/images/equations/WeakLawofLa
Solved (a) State and prove the weak law of large number. (b)

Laws of Large Numbers (detailed explanation), by Anirudh G

MATH2647 2015-2016 Lecture Notes - 3 Convergence of random variables - 2 Convergence of random - Studocu

Law of large numbers - Wikipedia
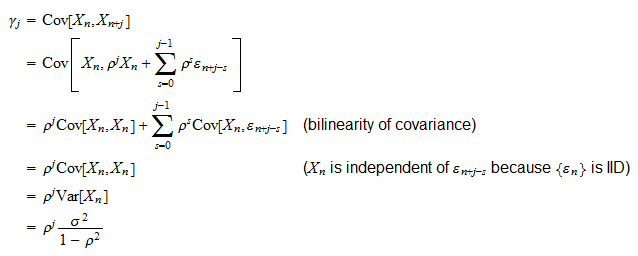
Law of Large Numbers Strong and weak, with proofs and exercises

Introduction to Mathematical Probability
Weak Law of Large Numbers Brief Guide to Weak Law of Large Number

Solved Problem 8 (Weak Law of Large Numbers). In this
Law of large numbers - Wikipedia

Weak Law of Large Numbers (WLLN). Overview, by Pablo Kowalski Kutz