U of T researchers find vulnerability in COVID-19 variants that
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that Omicron variants of the COVID-19-causing virus can be hindered in their ability to infect people by mutations in the spike protein that prevent the virus from binding to and entering cells.
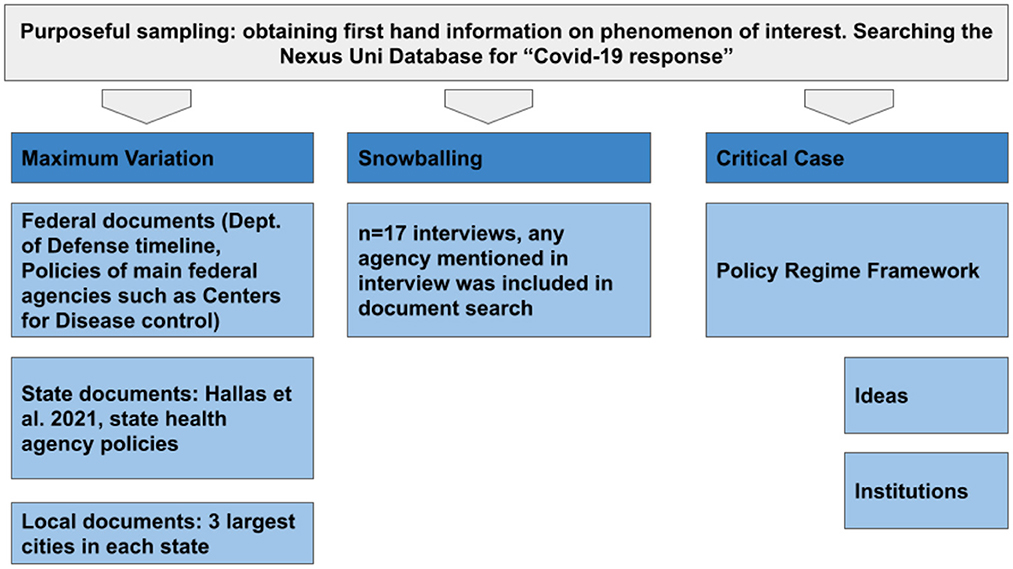
Frontiers Application of the Policy Regime Framework to understand COVID- 19 policy response in the Southeast U.S.: How RAPID research can provide lessons learned after a public health crisis
Infections with 'U.K. Variant' B.1.1.7 Have Greater Risk of Mortality – NIH Director's Blog
Temerty Faculty of Medicine

Effectiveness of BNT162b2 Vaccine against Critical Covid-19 in Adolescents

UBC researchers discover 'weak spot' in all major COVID variants - Victoria Times Colonist

Comparative analysis of within-host diversity among vaccinated COVID-19 patients infected with different SARS-CoV-2 variants - ScienceDirect
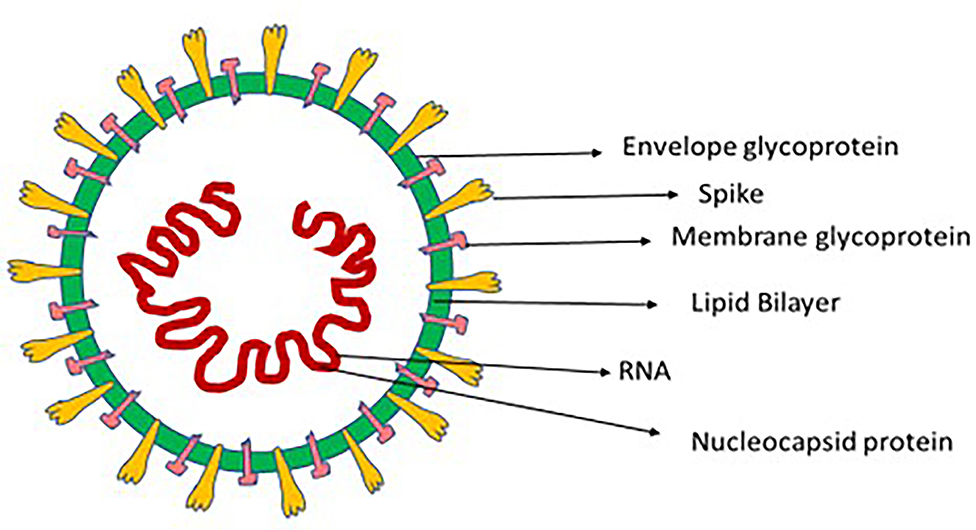
Frontiers Recent Chronology of COVID-19 Pandemic

Coronavirus Updates: Covid News: Fauci, Cautiously, Says, 50% OFF
Donnelly Centre Researchers Develop Rapid Test to Keep Track of Immunity to SARS-COV-2 Variants
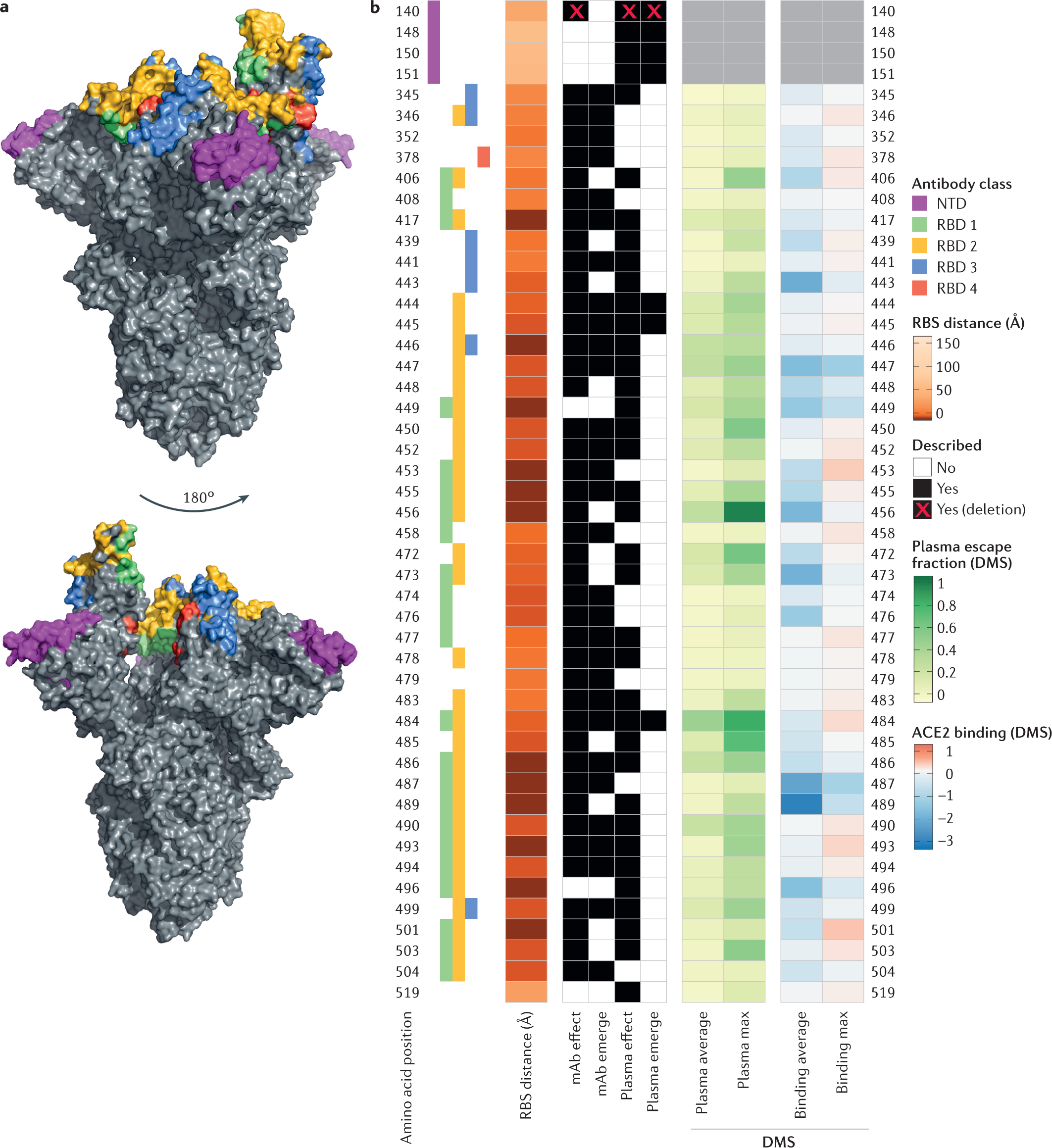
SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape

SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant Transmission Within Households — Four U.S. Jurisdictions, November 2021–February 2022
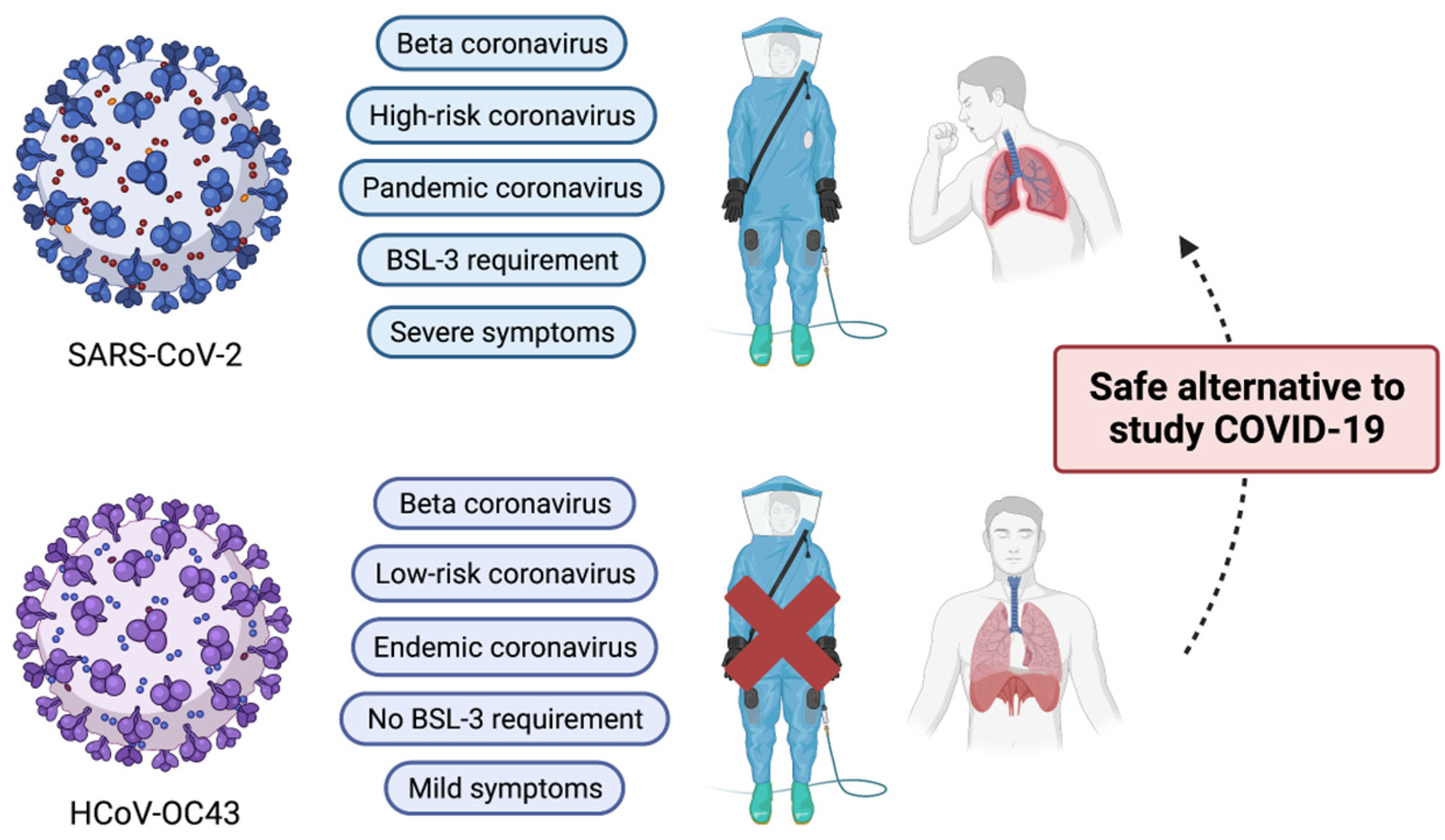
Viruses, Free Full-Text
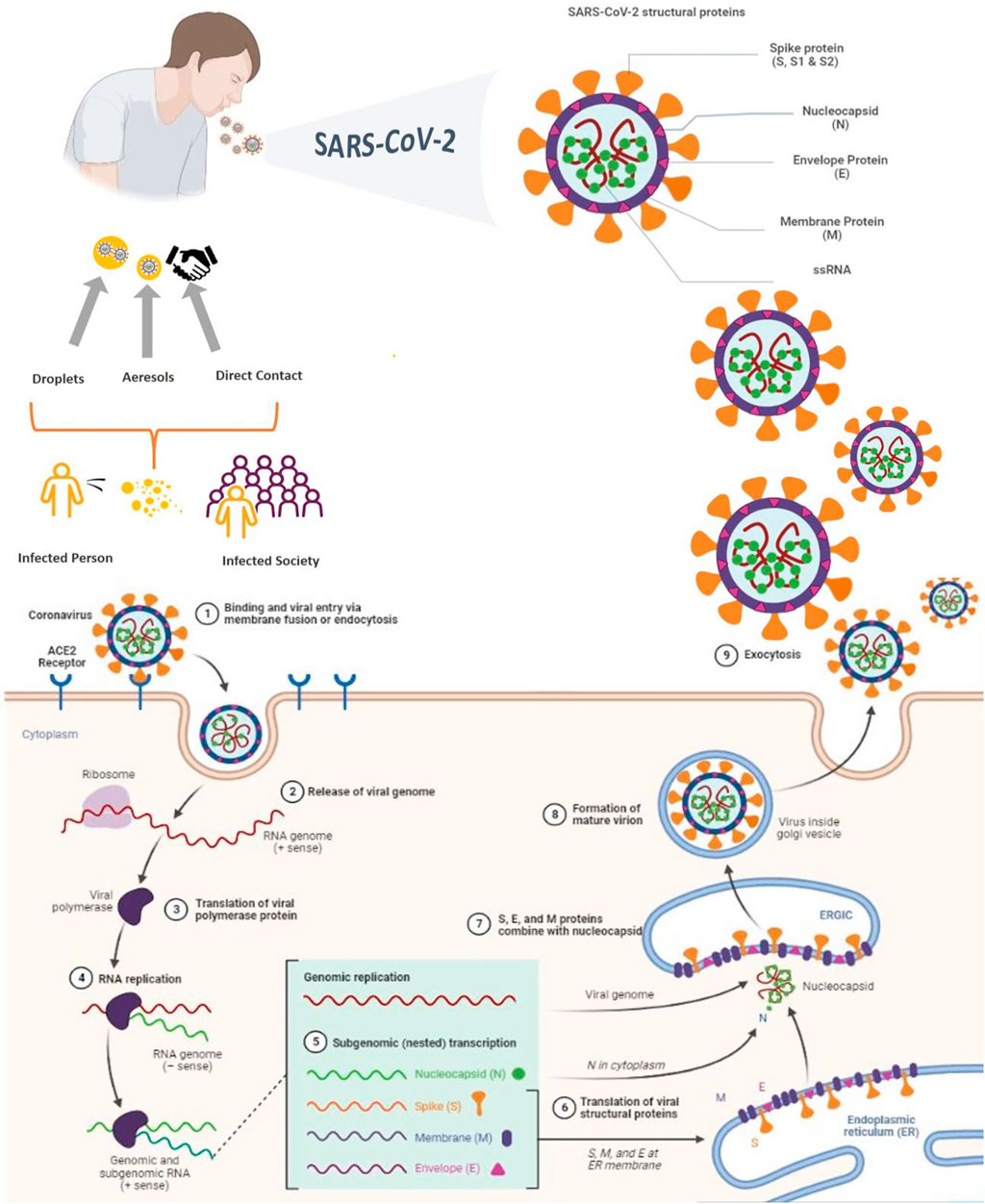
Frontiers Nanotechnology and COVID-19: Prevention, diagnosis, vaccine, and treatment strategies
Temerty Faculty of Medicine
Molecular Genetics University of Toronto