Tidal volume per kg body weight and mean inspiratory airflow. Calves

Download scientific diagram | Tidal volume per kg body weight and mean inspiratory airflow. Calves were either challenged with 108 inclusion forming units of C. psittaci or sham inoculated (controls). b.w, body weight; Vt, tidal volume. Data are expressed as Box-and-Whisker Plots representing lower and upper quartile values (box) with median and mean (+). Whiskers extend from each end of the box to the most extreme values within 1.5 interquartile ranges. Outliers are data beyond the ends of the whiskers. In calves inoculated with C. psittaci, # indicates a significant difference at the given time point compared to controls (Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon W test) at a probability level of p ≤ 0.01. Arrows (↑ or ↓) indicate significant increases or decreases, respectively, at the given time point compared to data ante inoculationem (a.i.) within the group (ANOVA, post hoc test: Bonferroni's multiple comparison procedure) at a probability level of p ≤ 0.01. from publication: Correction: Evaluation of pulmonary dysfunctions and acid–base imbalances induced by Chlamydia psittaci in a bovine model of respiratory infection | Backround Chlamydia psittaci (Cp) is a respiratory pathogen capable of inducing acute pulmonary zoonotic disease (psittacosis) or persistent infection. To elucidate the pathogenesis of this infection, a translational large animal model was recently introduced by our group. | Chlamydia, Inoculation and Psittacosis | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Detection of optimal PEEP for equal distribution of tidal volume
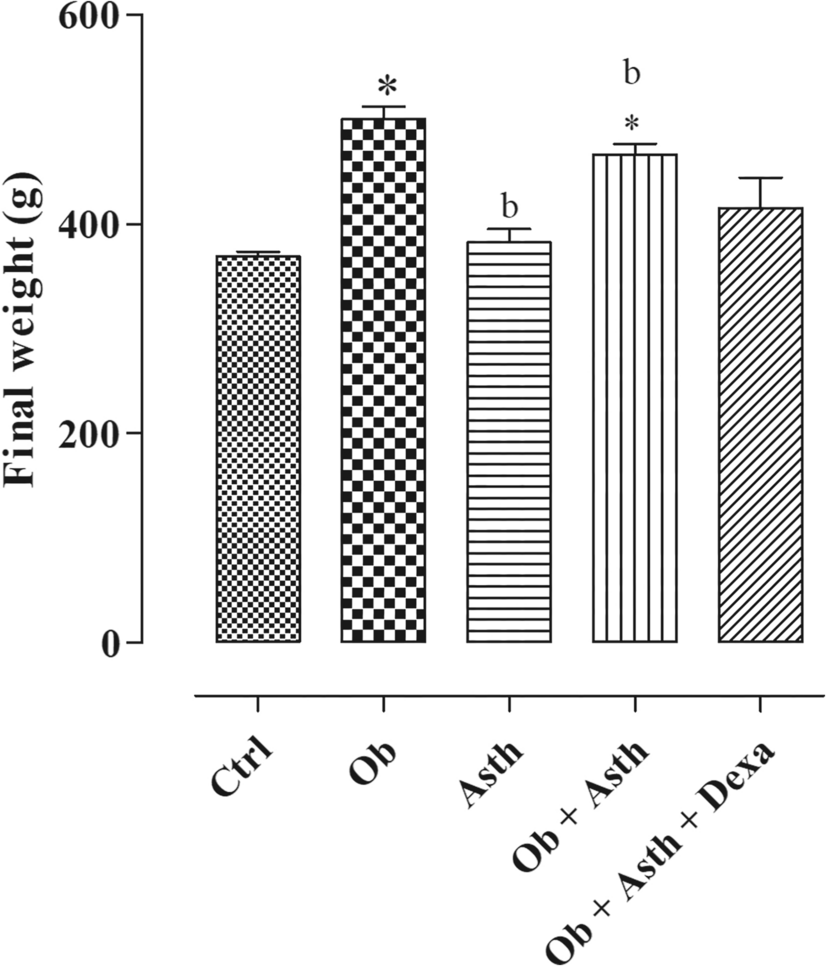
Functional and morphologic dysfunctions in the airways of rats
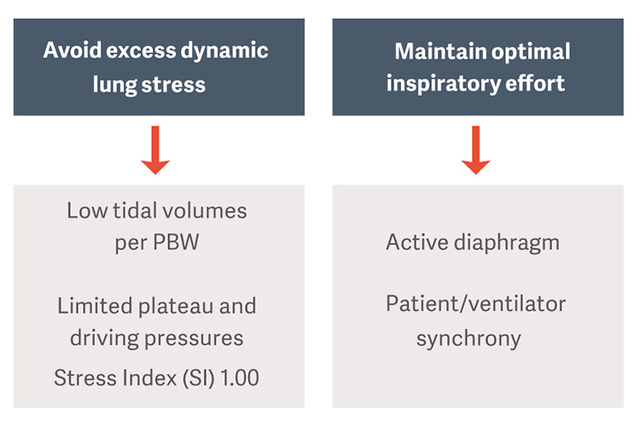
Early Protective Mechanical Ventilation is key to ARDS outcomes

What are the initial settings for assist-control (AC) volume cont
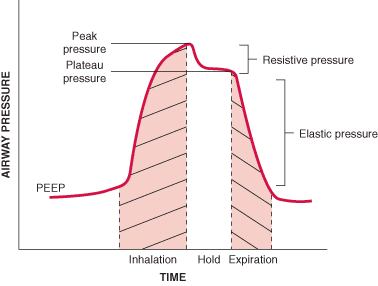
Overview of Mechanical Ventilation - Critical Care Medicine

Tidal breathing measurements. Tidal volumes, BPM, and I:E ratios

a) Example of a resting and peak exercise tidal breath

Postoperative prophylactic intermittent noninvasive ventilation

Tidal volume per kg of body weight according to inspiratory

Tidal volume per kg body weight and mean inspiratory airflow

The “spring model” illustrating the slinky effect of gravity on
Tidal volume and respiratory rate

Impact of Center of Admission on Receipt of Extracorporeal