Temperature Control: Convection Temperature Devices (-160 °C to +1000 °C)
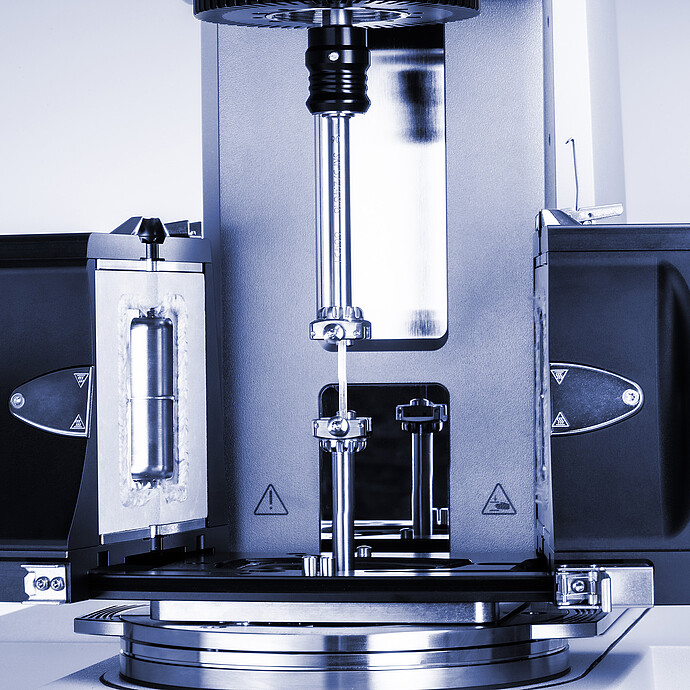

Temperature devices ideally suited for rheological measurements on melts, solids (torsion), and extensional rheology.
Perfect temperature control for measurements on melts and solids (DMA) and extensional rheology on films and fibers – the convection temperature devices for the MCR rheometer series make it happen. Due to their symmetric design, they guarantee an absolutely homogeneous temperature distribution and thus accurate and stable temperature control in all measuring systems, from parallel plates to solid bar fixtures, for optimal results when measuring polymer melts, glass melts, salt melts, metal melts, and solids. With their innovative design and comprehensive range of accessories, the convection temperature devices are a must for experienced rheologists.
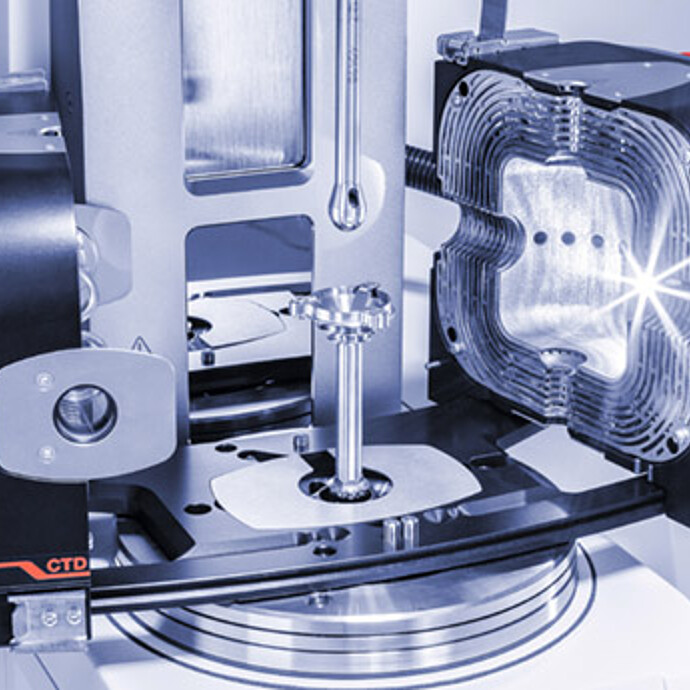
Temperature Control: Convection Temperature Devices (-160 °C to +1000 °C)

Diffusion of volatiles in hot stagnant-lid regime planets - ScienceDirect

Digital Temperature Controller Thermostat BBQ Grill Smoker Oven Stove baking cooking Charcoal Burning Cajun 300 °

Heat-Flex® Hi-Temp 1000

Inkbird All-Purpose Digital Temperature Controller Fahrenheit &Centigrade Thermostat w Sensor 2 Relays (ITC-1000).: : Industrial & Scientific

Heat Transfer, PDF, Heat Transfer
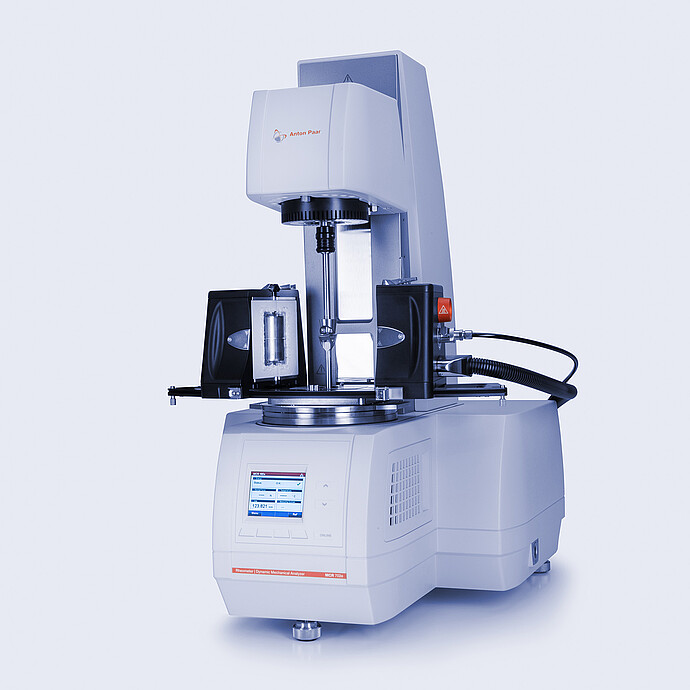

Temperature Control: Convection Temperature Devices (-160 °C to +1000 °C)
Stable and reliable, the shell is made of flame‑retardant ABS material, which will not be easily damaged Alarm function: With sound and light alarm

Cooling and Heating Temperature Controller, Digital Temperature Controller, ABS Flame Retardant Plastic Shell ‑50℃ to 110℃ Cooling, Convection Ovens

Inkbird All-Purpose Digital Temperature Controller Fahrenheit &Centigrade Thermostat w Sensor 2 Relays (ITC-1000).: : Industrial & Scientific

C92IP001EN-P Brochure MCR Evolution Series Screen, PDF, Materials Science

TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT IN INDUSTRIAL ENVIRONMENTS

Diffusion of volatiles in hot stagnant-lid regime planets - ScienceDirect