File:CPR Adult Chest Compression.png - Wikimedia Commons

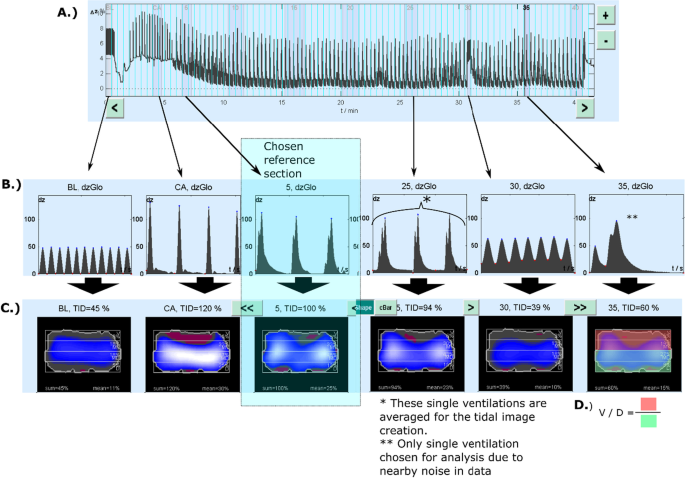
Ventilation during continuous compressions or at 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio results in similar arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in an experimental model of prolonged cardiac arrest, Intensive Care Medicine Experimental
How to Perform Adult CPR
Continuous chest compressions are associated with higher peak inspiratory pressures when compared to 30:2 in an experimental cardiac arrest model, Intensive Care Medicine Experimental

Evaluation of manual chest compressions according to the updated cardiopulmonary resuscitation guidelines and the impact of feedback devices in an educational resuscitation course, BMC Emergency Medicine

Adequacy of compression positioning using the feedback device

Comparison of CPR quality and rescuer fatigue between standard 30:2 CPR and chest compression-only CPR: a randomized crossover manikin trial – topic of research paper in Medical engineering. Download scholarly article PDF
PDF) Quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest before and after introduction of a mechanical chest compression device, LUCAS-2; a prospective, observational study

The intra-arrest carotid blood flow during CPR. CBF, carotid blood

– Emergency Medicine EducationUS Probe: Preventing
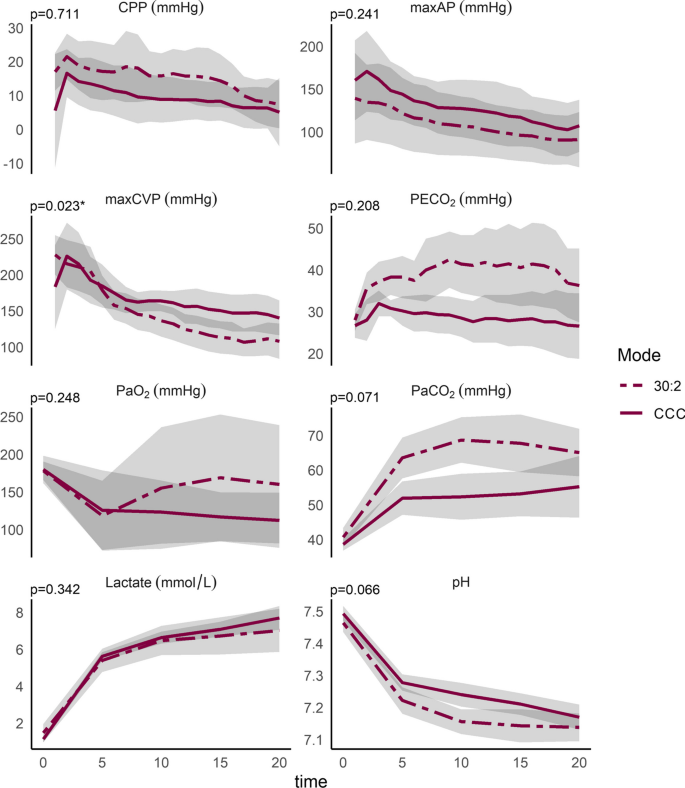
Continuous chest compressions are associated with higher peak inspiratory pressures when compared to 30:2 in an experimental cardiac arrest model, Intensive Care Medicine Experimental

Age-stratified comparison of the participants' CPR performance in
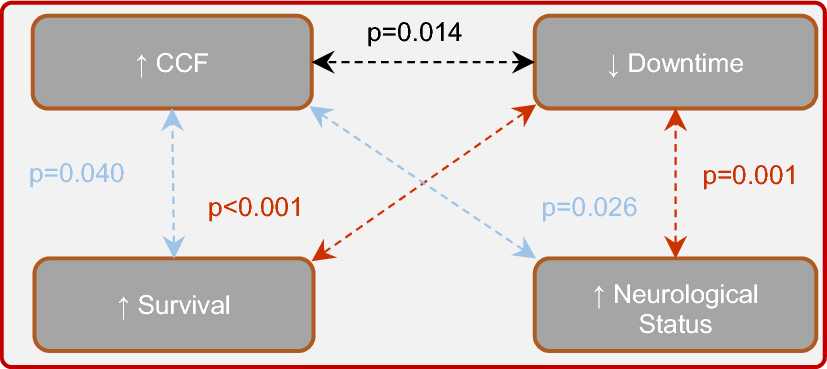
Chest compression quality and patient outcomes with the use of a CPR feedback device: A retrospective study

File:Cpr-mask-placement.png - Wikimedia Commons

History of cardiopulmonary resuscitation - Wikipedia

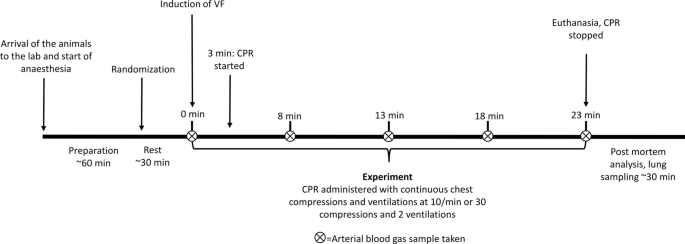
Model depicting data collection during CPR